Table of contents
When I was using console.log() for an object in the browser console, that is when I first encountered the word “prototype” in JavaScript.
PermalinkPrototype
A prototype is an object associated with every function and object by default in JavaScript. The function's prototype property is accessible and adaptable and the object's prototype property is not visible.
Every function includes a prototype object by default.
You can see the prototype an object is pointing to using the proto property.
The prototype object is a particular type of enumerable object to which additional properties can be attached, which will be shared across all the instances of its constructor function.
function Student() {
this.name = 'John';
this.gender = 'M';
}
Student.prototype.age = 15;
var studObj1 = new Student();
alert(studObj1.age); // 15
var studObj2 = new Student();
alert(studObj2.age); // 15
PermalinkPrototype Chaining
Prototypes are the means of inheritance in JavaScript. The prototype of an object would also have a prototype object. This continues until we reach the top level when there is no prototype object.
This is called prototype chaining or prototype chain in JavaScript.
The properties defined on the prototype objects are also accessible to the object instance. And this is the reason why we are able to access properties that we have not defined explicitly on an object since those are accessible by inheritance through the prototype chaining.
When we try to access any property of an object it is first checked in the own property of the object.
If the property does not exist in the property, then the prototype object is scanned for that property. This continues until we get the property we are accessing or we reach the end of the prototype chain giving undefined.
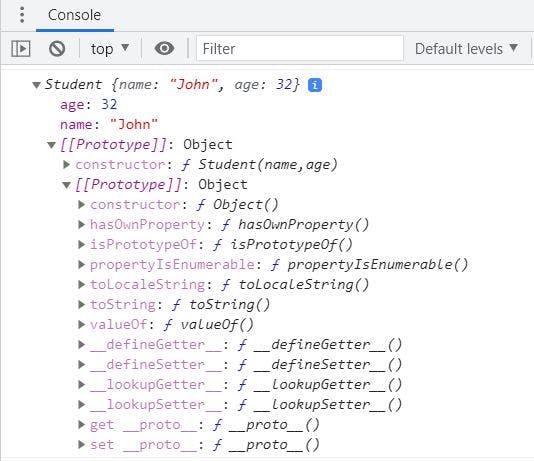
// defining the constructor function
function Student(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// creating an object instance of the Student
const student = new Student('John',32)
console.log(student)
PermalinkOutput
Thank you for reading ❤️